Within the realm of medical diagnostics, innovation is aware of no bounds. Just lately, an thrilling breakthrough has emerged on the intersection of laptop imaginative and prescient and machine studying, promising to revolutionize the best way we assess and consider sufferers, notably these with motor problems comparable to cerebral palsy. This groundbreaking growth, often called the Pose-Mapping Technique, is about to reshape the panorama of medical prognosis and affected person care.
Historically, evaluating sufferers’ motor perform, particularly for circumstances like cerebral palsy, necessitates frequent in-person visits to the physician’s workplace. This course of might be not solely cumbersome but additionally financially burdensome and emotionally taxing, notably for youngsters and their dad and mom. Nevertheless, because of this cutting-edge method developed by MIT engineers, we’re now on the cusp of a transformative leap ahead in medical evaluation.
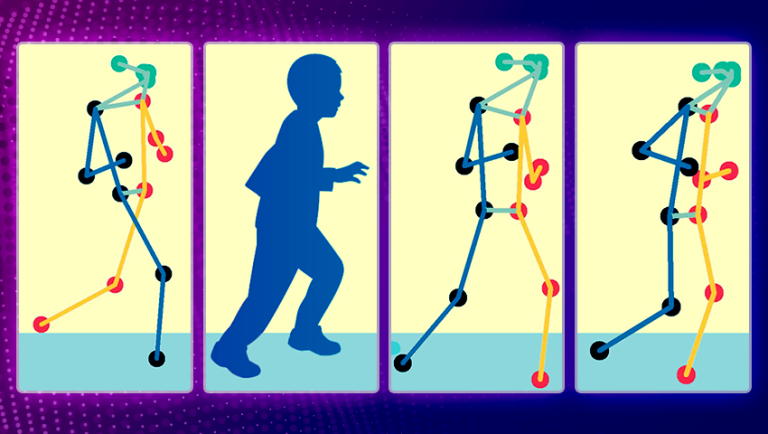
On the coronary heart of this innovation lies the seamless integration of laptop imaginative and prescient and machine studying. By harnessing these superior applied sciences, the Pose-Mapping Approach has unlocked the potential to remotely assess sufferers’ motor perform. The tactic analyzes real-time movies of sufferers, deciphering particular patterns of poses inside these movies. This evaluation, pushed by machine studying algorithms, computes a scientific rating of motor perform.
To develop a way for analyzing skeleton pose information in sufferers with cerebral palsy, a situation usually assessed utilizing the Gross Motor Perform Classification System (GMFCS), scientists make use of a five-level scale representing a baby’s general motor perform (decrease numbers point out greater mobility).
The group used a publicly out there set of skeleton pose information supplied by Stanford College’s Neuromuscular Biomechanics Laboratory. This dataset contained movies that includes over 1,000 youngsters with cerebral palsy, every demonstrating varied workouts in a scientific atmosphere. Moreover, every video was tagged with a GMFCS rating assigned by a clinician following an in-person evaluation. The Stanford group processed these movies by a pose estimation algorithm to generate skeleton pose information, serving as the inspiration for MIT’s subsequent examine.
Remarkably, the Pose-Mapping Approach exhibited an accuracy charge exceeding 70% that matches the assessments of clinicians throughout in-person evaluations. This stage of precision holds immense promise for streamlining affected person assessments and decreasing the necessity for frequent and arduous journeys to medical services.
The potential functions of the Pose-Mapping Approach lengthen far past cerebral palsy. The analysis group is at present tailoring the strategy to judge youngsters with metachromatic leukodystrophy, a uncommon genetic dysfunction affecting the nervous system. Moreover, they’re actively engaged on adapting the strategy to evaluate sufferers who’ve skilled a stroke.
Hermano Krebs, a principal analysis scientist at MIT’s Division of Mechanical Engineering, envisions a future the place sufferers can cut back their reliance on hospital visits for evaluations. “We predict this expertise may doubtlessly be used to remotely consider any situation that impacts motor conduct,” he says. This suggests a seismic shift in the best way we strategy medical assessments and affected person care.
The street to this exceptional achievement started with laptop imaginative and prescient and algorithms designed to estimate human actions. Pose estimation algorithms paved the best way for the interpretation of video sequences into skeleton poses. These poses, represented as strains and dots, had been then mapped to coordinates for additional evaluation.
The analysis group leveraged a Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolutional Neural Community to decipher patterns in cerebral palsy information, classifying sufferers’ mobility ranges. Astonishingly, coaching the community on a broader dataset, which included movies of wholesome adults performing each day actions, considerably enhanced its accuracy in classifying cerebral palsy sufferers.
The true marvel of this innovation is its accessibility. The tactic might be seamlessly executed on a mess of cell units, guaranteeing widespread availability and real-time processing of movies. The MIT group is actively creating an app that would empower sufferers to take management of their self-assessments. This app would enable dad and mom and sufferers to file movies throughout the consolation of their properties. The outcomes may then be shared effortlessly with healthcare professionals, paving the best way for extra knowledgeable and well timed interventions. Furthermore, the strategy’s adaptability extends to evaluating different neurological problems, promising to cut back healthcare prices and improve affected person care.
As was talked about, the combination of laptop imaginative and prescient and machine studying is quickly remodeling the panorama of medical diagnostics. At QuData, we share this enthusiasm for revolutionary options in medical imaging, contributing to a brighter future for healthcare. Our case studies provide a closer look at our ML research and solutions. Learn extra about our newest mission Breast Cancer Computer-Aided Detection – AI-driven answer for enhancing breast most cancers prognosis precision and effectivity.