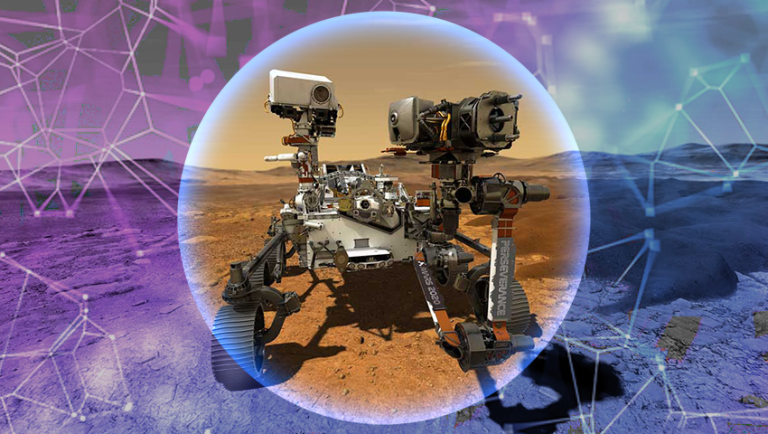
As we all know, NASA’s Perseverance rover continues its mission on Mars. It explores the planet’s panorama, assesses its pure assets, and collects samples of Martian rocks and ambiance, amongst different duties.

Perseverance rover. Credit: NASA
Perseverance is provided with a system for gathering and storing soil samples, which makes use of rotary percussion drilling expertise. On the finish of the rover’s 2m robotic arm is a rotary percussion drill and a hole borehole for simultaneous floor drilling and sampling. Perseverance can also be outfitted with 43 titanium tubes designed to retailer the samples, with 5 of them remaining empty for purity management functions.
The gathering of soil samples takes place within the Jezero Crater on Mars. Billions of years in the past, this location was a lake, with a river flowing into the crater. The river introduced sediment and fashioned a steep fan-shaped delta. It’s assumed that helpful details about historic Martian biology could be extracted from the rock deposits discovered right here.
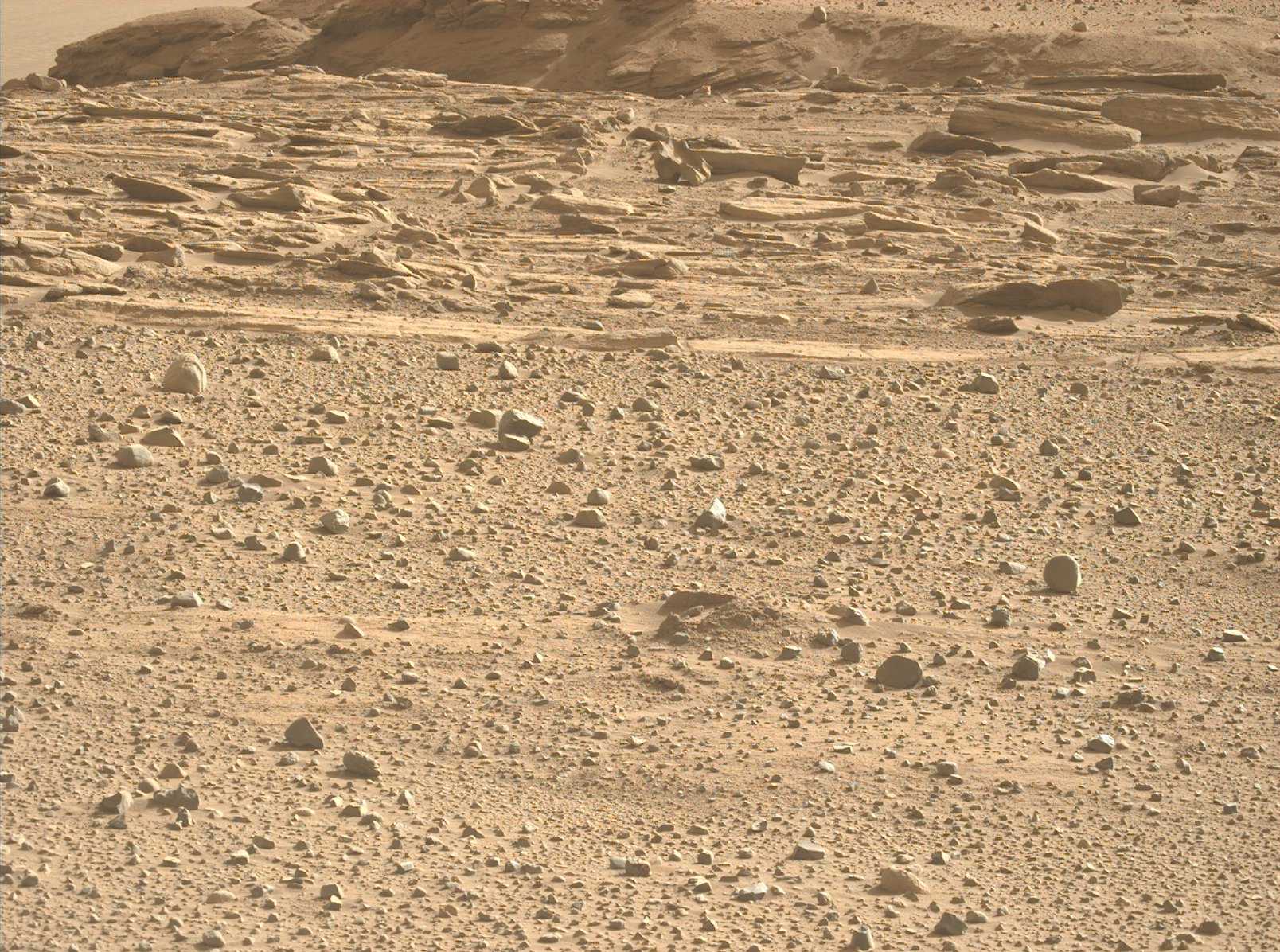

Jezero Crater. Credit: NASA
Perseverance drills into the chosen pattern, extracts materials from it, locations the pattern in a container, and seals it securely. The rover collects two samples of every rock sort. The concept is to go away one pattern on board and discard the opposite for storage at specifically marked places throughout the Three Forks space contained in the Jezero Crater. It will function a backup storage in case one thing occurs to the rover and it’s unable to ship the containers.
The pattern container itself is a particular hermetic titanium tube 15.24 cm (6 inches) lengthy. Retrieving every container from inside Perseverance takes over an hour, after which the rover rigorously deposits the container within the pattern storage zone on Mars.
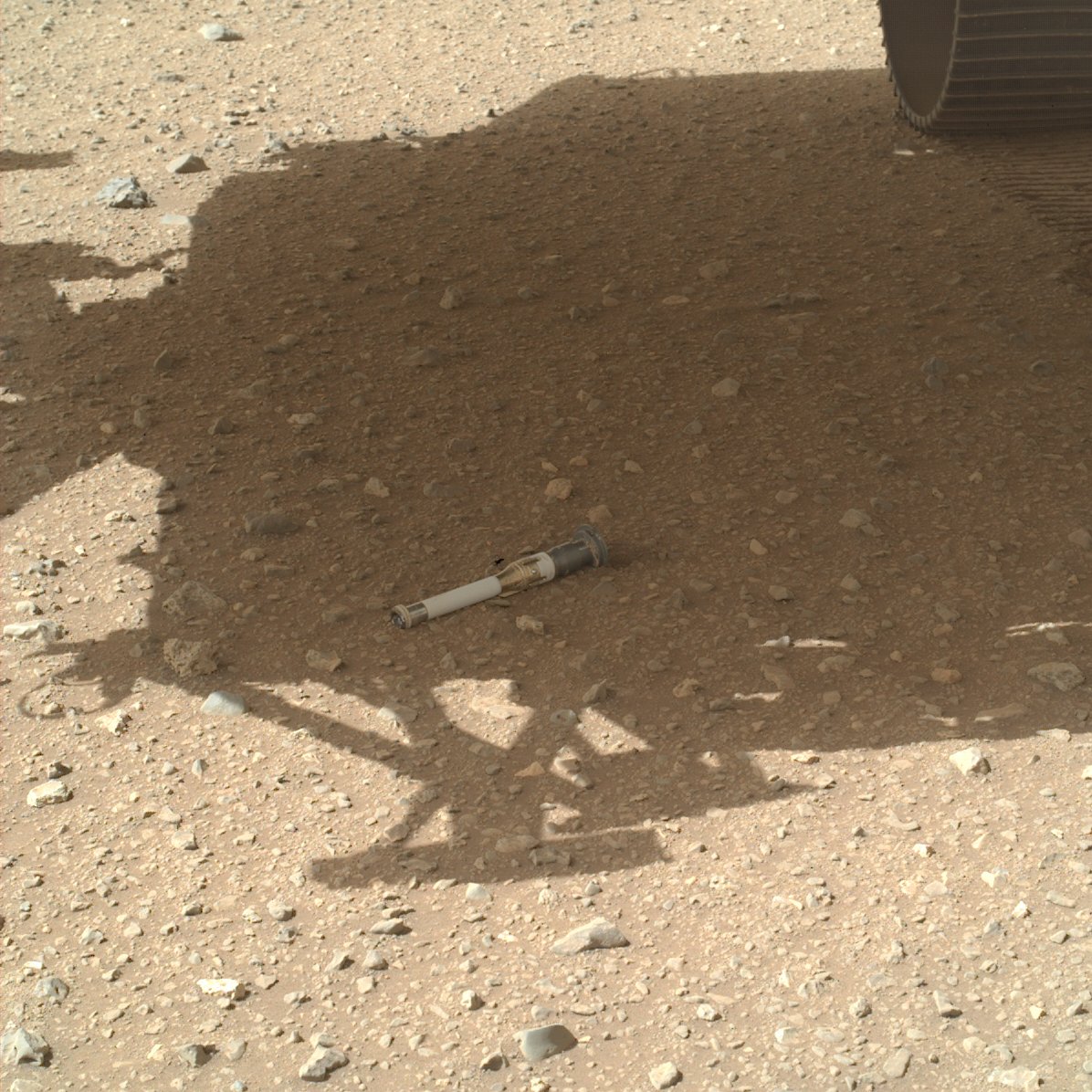

A pattern taken from igneous rock close to the Perseverance touchdown space. Credit: NASA
NASA has a website for the pattern assortment, which shows the method of fabric assortment and supplies detailed details about every pattern.
Martian rock samples collected by the Perseverance rover. Credit: NASA
The coordinates of every drop-off level are recorded in order that Perseverance can return to them if wanted. The samples are saved within the open, spaced aside from one another. The position factors had been particularly chosen to permit straightforward retrieval by the robotic arm of the rover or by a future mission, probably by helicopters, in case the rover malfunctions.
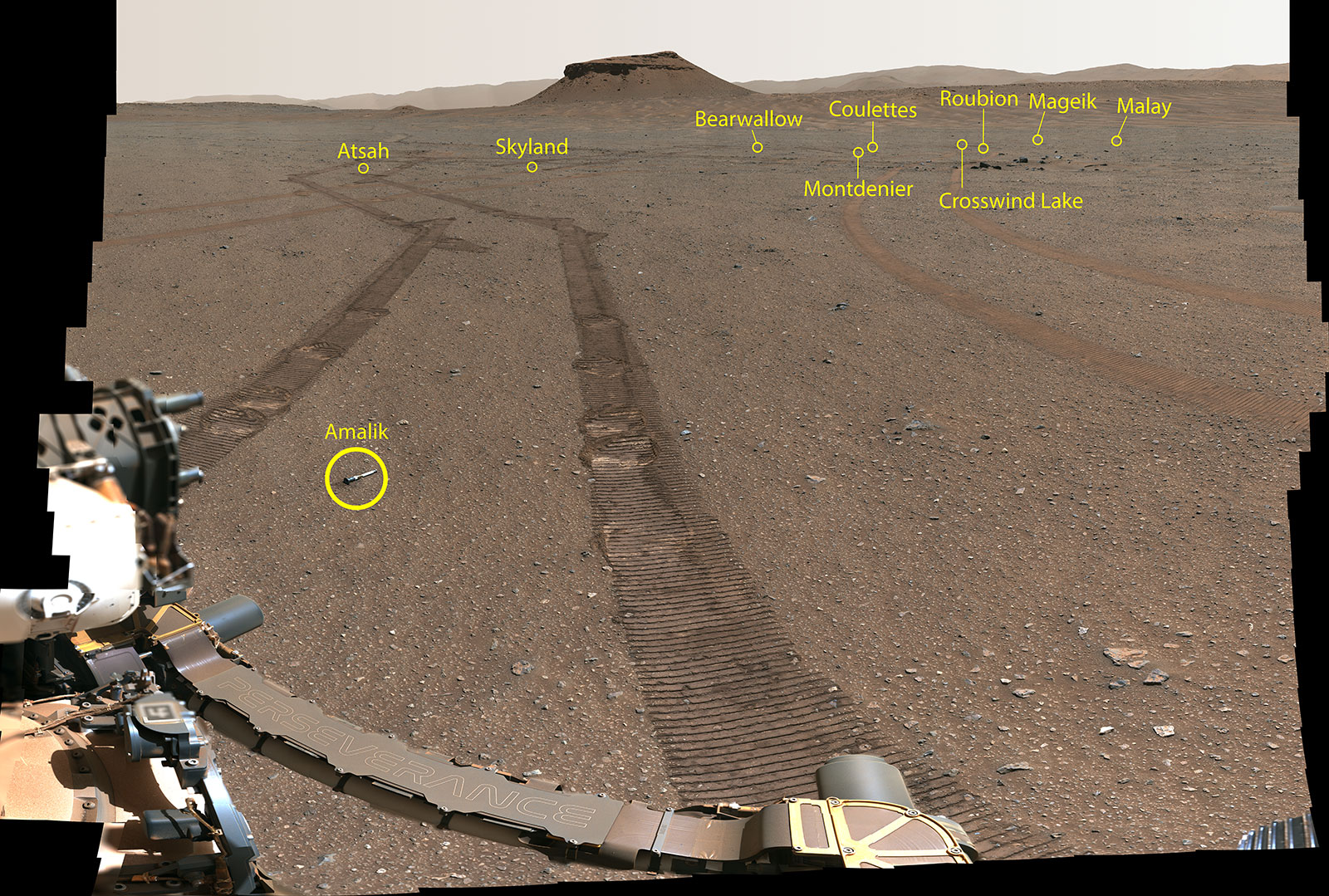

Ten pattern tubes left for the Mars Pattern Return Marketing campaign. Credit: NASA
Returning samples from Mars to Earth is taken into account to be probably the most complicated marketing campaign of robotic area exploration ever undertaken. The Pattern Fetch Rover, developed as a joint mission of the European House Company (ESA) and Roscosmos, was supposed to be a part of this marketing campaign. Nonetheless, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine led to the cancellation of this system. ESA refused to launch the venture on a Soyuz rocket. The mission was placed on maintain. Nonetheless, the underlying expertise stays essential for the Mars Pattern Return Marketing campaign.
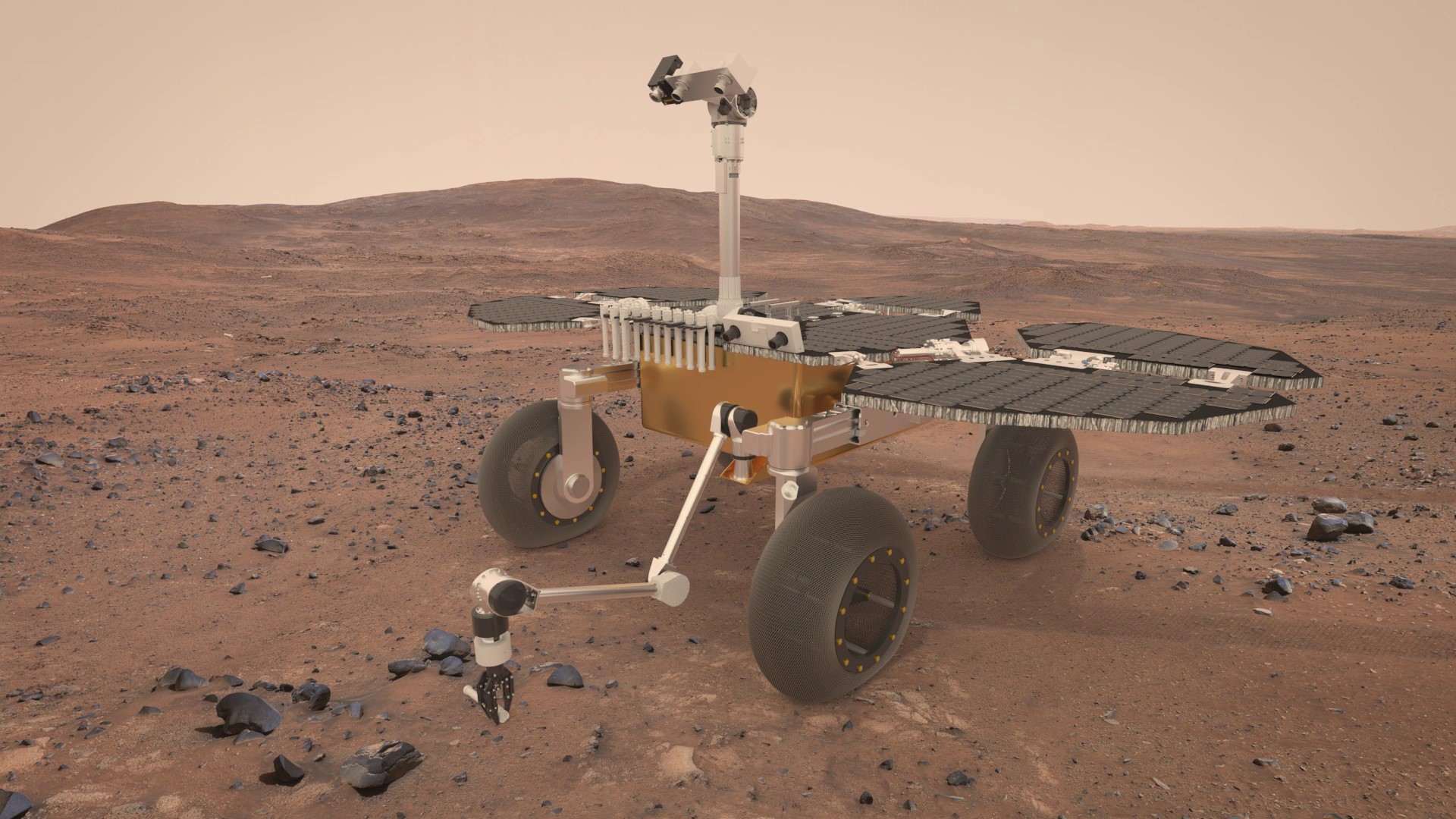
Pattern Fetch Rover. Credit: ESA
Laura Bielenberg, an ESA graduate trainee, is engaged on an experimental setup referred to as Rabbit (RAS Bread Boarding In-house Testbed). Right here, a precise duplicate of the gathering system that was speculated to be a part of ESA Pattern Fetch Rover is being reproduced. The pattern switch arm remains to be wanted to load the titanium tubes with Martian samples and transport them to Earth. The robotic arm of ESA will accumulate them from the Perseverance rover and, presumably, from sample recovery helicopters as backup.
The work is being carried out on the Mars Yard check web site, which is a part of ESA’s Planetary Robotics Laboratory at ESA ESTEC technical heart in Noordwijk, Netherlands. Right here, the Martian rocky panorama is precisely recreated.
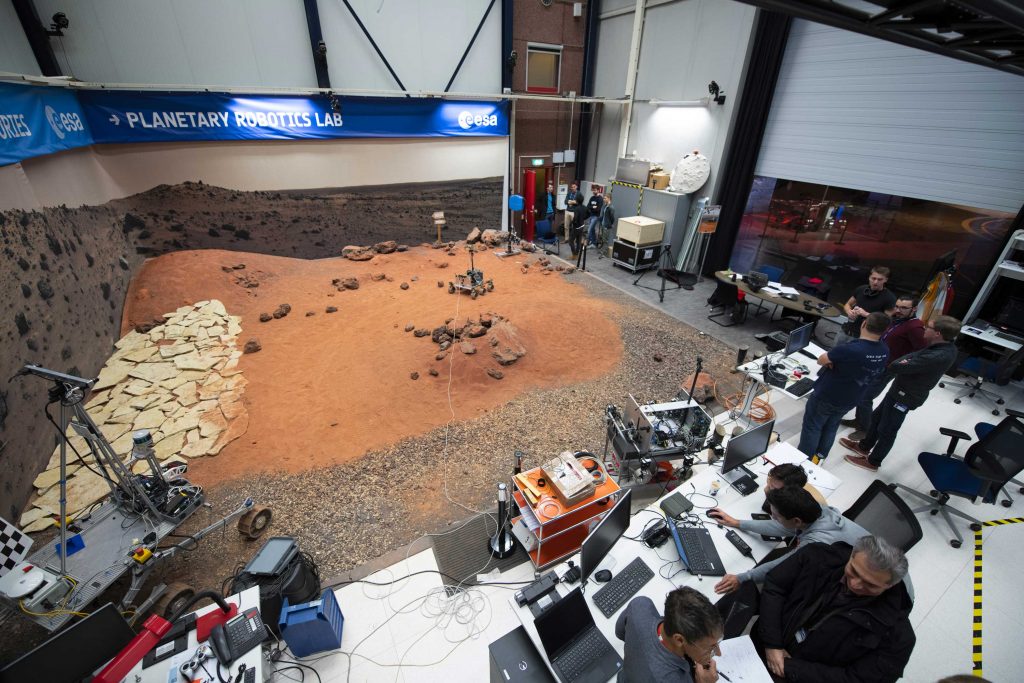

Mars Yard at ESA’s technical heart within the Netherlands. Credit: ESA
Laura leaves copies of the titanium tubes for samples on the floor of the check web site close to the metallic construction with the robotic arm and explores methods for his or her assortment, from autonomous detection to estimating the place of the pattern tubes on Mars.
To detect tubes and estimate their place and orientation, the workforce of scientists makes use of not solely cameras and sensors, but additionally neural networks. The neural community algorithm was developed in collaboration with Katholieke Universiteit Leuven in Belgium.
The tube assortment setup is provided with a navigation digital camera put in on high of the construction. The neural community receives photographs from this digital camera and searches for the titanium tubes in them. It additionally identifies factors within the picture to evaluate the place of the tube on the floor.
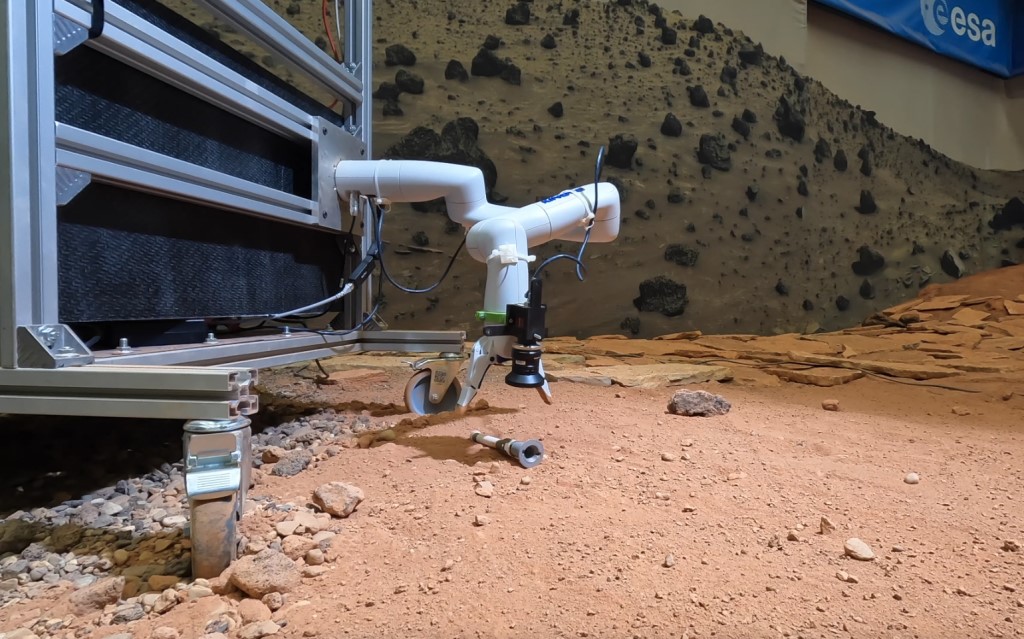

Testing pattern tube assortment methods for Mars. Credit: ESA
The workforce tried to recreate the Martian atmosphere, simulating comparable lighting and panorama circumstances. A mix of direct and oblique lighting was designed, and imitation of several types of terrain was achieved by combining sand, pebbles and stones. All these actions had been taken to enhance the standard of neural community coaching.
The objective of the mission is to ship samples from Mars to Earth. The information obtained from these samples and the applied sciences developed as a part of Mars exploration packages, will sooner or later assist humanity to unravel the mysteries of the Crimson Planet.